Issue: Material is classified as 7.2 and must not contain 80% or more of substances in the Chk: Classification 1-4 w/o silver, gold
The material in question is classified as 7.2 – Ceramics / glass; but contains more than 80% or more of substances in the Basic Substance Group Chk: Classification 1-4 w/o silver, gold.¹
Per IMDS Recommendation 001a² – 7.2 classification for UVCB materials (unknown or variable composition, complex reaction products or biological materials) like glass, silicate ceramic, and enamel as well as technical ceramics such as ferrites, silicon carbides and boron nitride. You can check for the groups a substance belongs to by highlighting the substance in the tree structure.
Note: In 2013 the IMDS Steering Committee adopted a new methodology for representing ceramic, glass and enamel (hereinafter glass) materials in IMDS. The change is explained in IMDS Recommendation 001a, Section 2.6 MDS creation for glass, silicate ceramic and enamel.
As part of that change, three new pseudo-substances were added to IMDS:
- Glass without declarable substances
- Enamel without declarable substances
- Ceramic without declarable substances
To more accurately represent glass composition, IMDS added the pseudo-substances listed above to replace the oxides traditionally shown for the composition of glass. However, IMDS’s primary focus is tracking declarable substances. As a compromise between the results of the physical and chemical changes that turn oxides into glass and the need to track regulated substances, IMDS requires that if an element contributed by any of the oxide substances is listed on the GADSL, it must be declared in the glass formulation in IMDS. For example, Lead monoxide (PbO) contributes Pb to a glass material and Pb is listed on the GADSL. Lead should be shown in the formulation of the glass in IMDS. The oxygen (O) in the PbO is not declarable and is represented within the Glass without declarable substances pseudo-substance.
The decision tree below will help you decide which elements in the oxides can be included in the pseudo-substance and which must be listed separately. There may be additional elements that you wish to list separately because they need to be traceable for non-GADSL reasons. For example, the Conflict Mineral substances (tin, tantalum, tungsten and gold) are not on the GADSL but for compliance with the U.S. Conflict Minerals law, it is important to be able to trace them in your IMDS data.
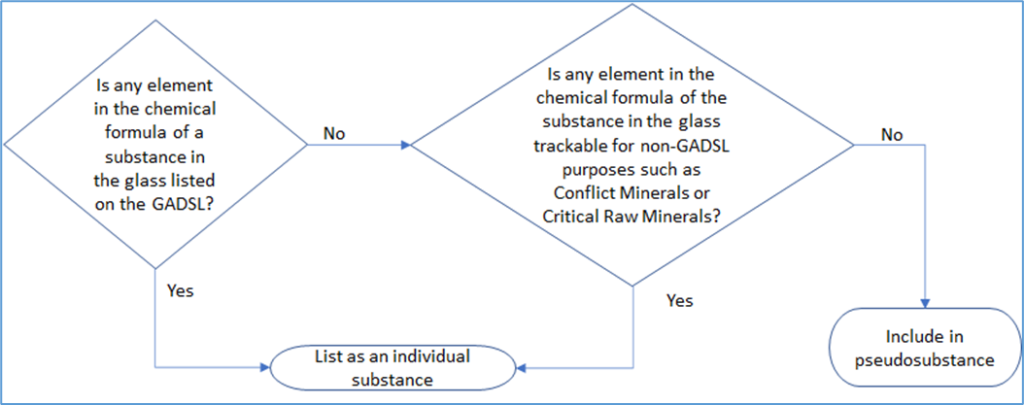
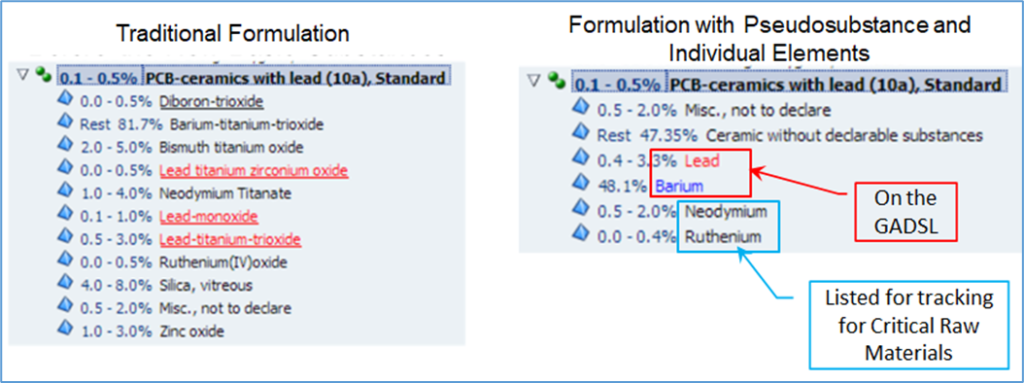
Below is an example of applying the decision tree above to a traditional listing of oxides to make a new style glass material in IMDS.
Action Required:
Review the material composition and classification and revise as necessary. If necessary, revise this material to meet the current requirements of IMDS for UVCB materials per IMDS Recommendation 001a, Section 2.6 MDS creation for glass, silicate ceramic and enamel. In order to revise a glass material to meet the 2013 IMDS criteria, you must perform a stoichiometric analysis of the glass formulation. The results of the analysis will tell you which substances are lumped into one of the pseudo-stances above and which are required to be declared. It is possible that a substance in the original formulation does not need to be declared while one of its constituent elements does. Any constituent element that is listed on the GADSL must be declared when revising the glass formulation to meet the 2013 requirements. You can learn more about how to do a stoichiometric analysis here: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=7pmgbu2CRs4. The following website will assist with the analysis by calculating the percentage of each element in a molecule: https://www.webqc.org/mmcalc.php.
¹ You can find the substances included in a basic substance group by searching for the group members in the substance search in IMDS.
² IMDS Recommendations may be downloaded from inside IMDS at Help > Recommendation.